No.31 Rui-Li Zhang, Shu Li, Stephen Maciejewski&Yi-Gang Wei
Petrocodonrubiginosus, a new species of Gesneriaceae from Guangxi,
PhytoKeys:doi: 10.3897/phytokeys.@.32270
Abstract
Petrocodonrubiginosus Y.G. Wei & R.L. Zhang, sp. nov., from Guangxi of South China, is described and illustrated with photographs. The new species is morphologically similar to Pet. hechiensis, but can be easily distinguished by a combination of characters, especially in its petioles, peduncles and pedicels covered with densely ferruginous pilose hairs.
Original Link:http://phytokeys.pensoft.net
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/336328177_Petrocodon_rubiginosus_a_new_species_of_Gesneriaceae_from_Guangxi_China

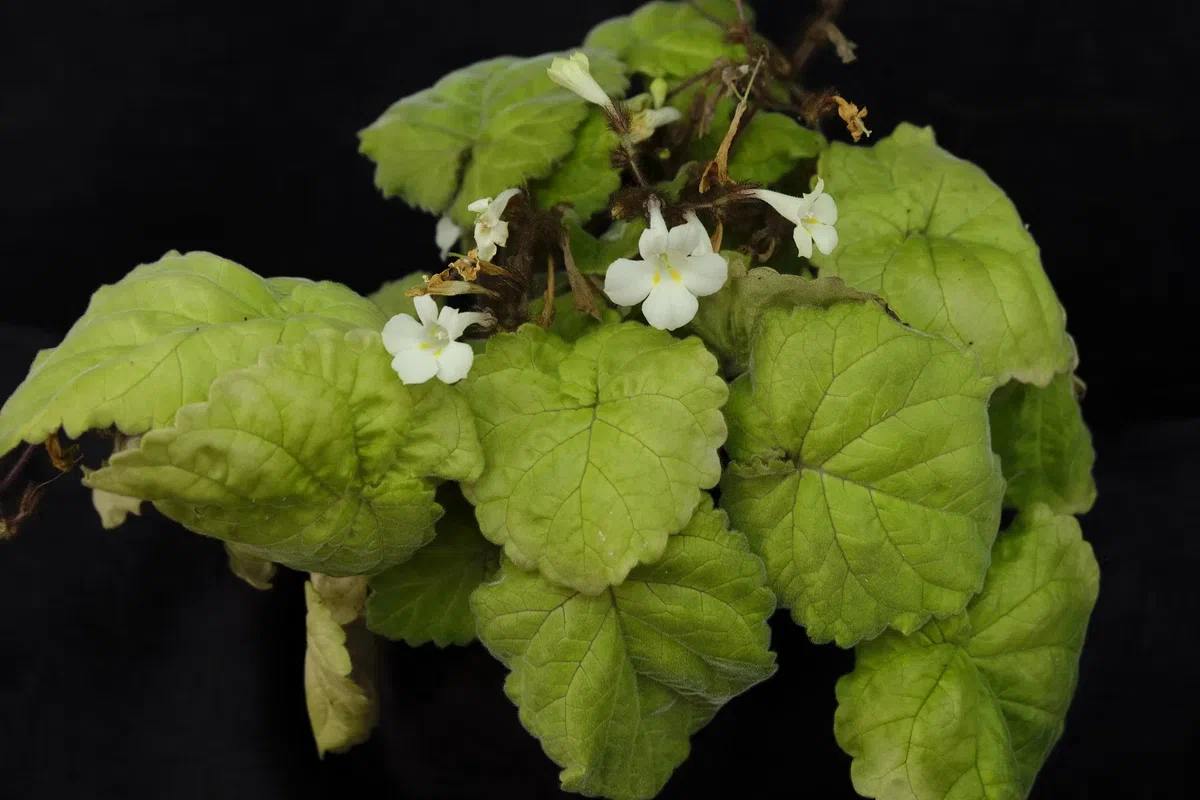
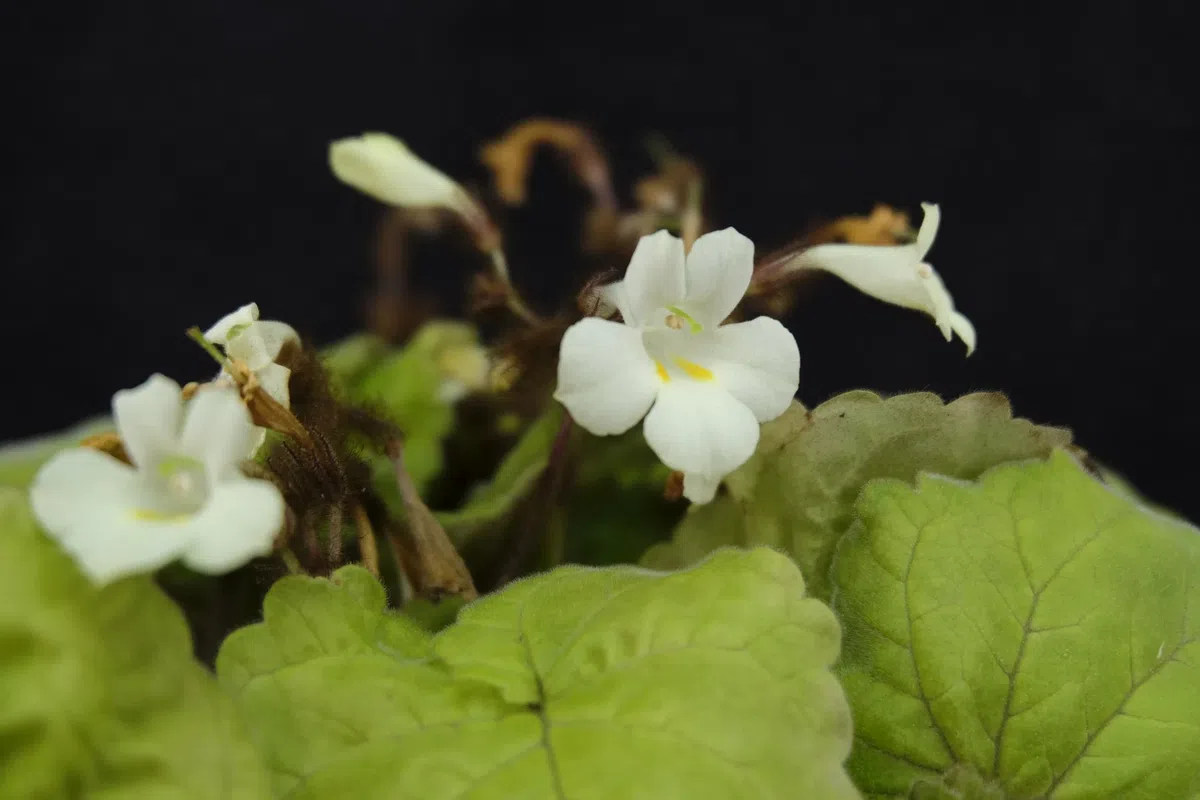
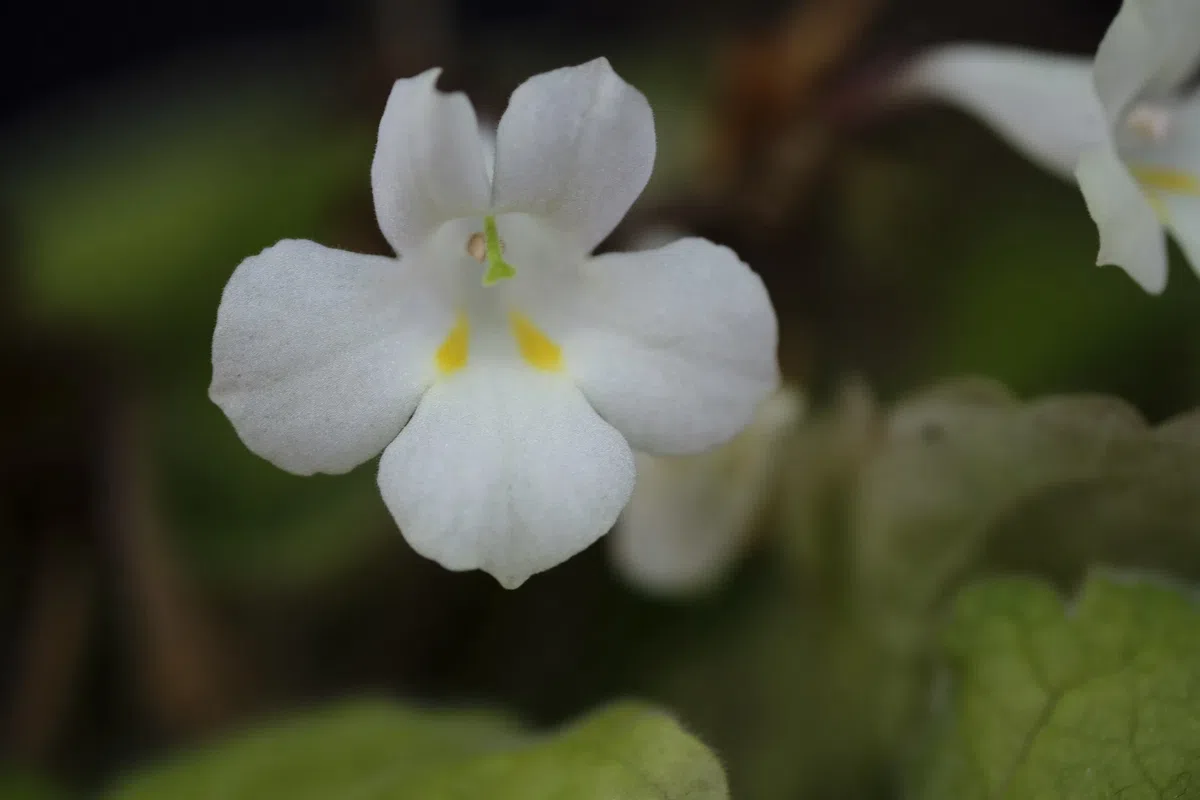
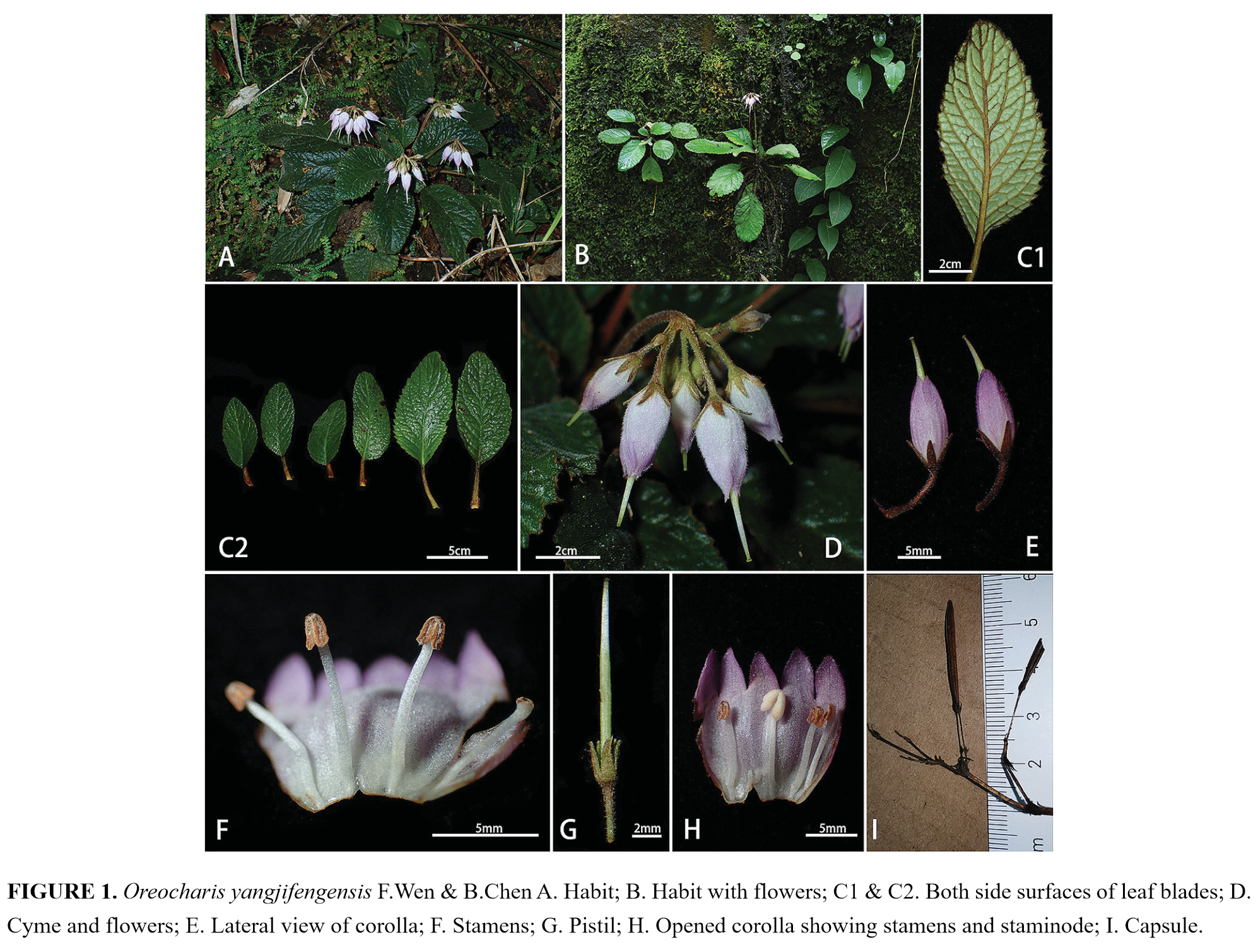
Figure 1. PetrocodonrubiginosusY.G.Wei&R.L.Zhang, sp. nov.A flowering plant in natural habitat (Jingxi, Guangxi, China) B flowering plant cultivated in GCCC C cyme D corolla in front view E corolla in lateral view and bud on cyme F indumentum of peduncle G flower in top view H flower in lateral view I flower in upward view J resolved flower for showing corolla, calyx lobes, pistil and pedicel K pistil and calyx lobes (adaxial & abaxial surfaces) L style and stigma. Photographs by authors.
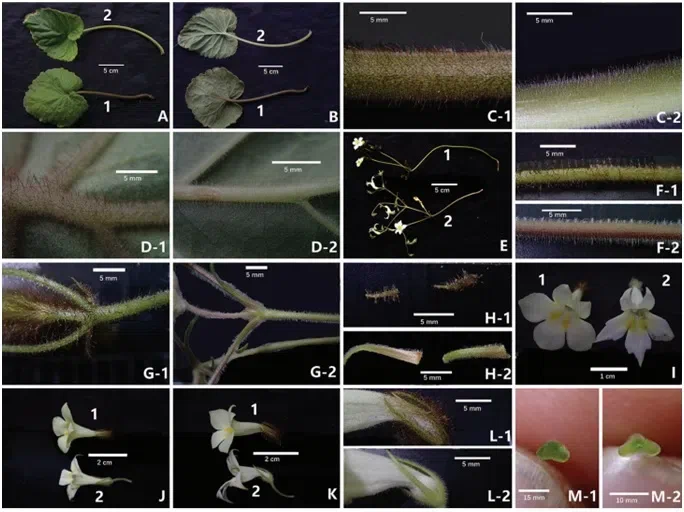

Figure 2. PetrocodonrubiginosusY.G.Wei&R.L.Zhang, sp. nov. (1) and its congener, Pet. hechiensis(Y.G.Wei, Yan Liu &F.Wen) Y.G.Wei&Mich.Möller (2) A adaxial surfaces of leaf blades and petioles of two species B abaxial surfaces of leaf blades and petioles of two species C indumentum of petioles D indumentum of main nerves on adaxial surface E cymes and flowers F indumentum of pedunclesG indumentum of bracts and pedicels H abaxial and adaxial surfaces of bracts I corolla in frontal views J corolla in top views K corolla in lateral views L indumentum of abaxial surfaces of calyx lobes M stigma. Photographs by authors.
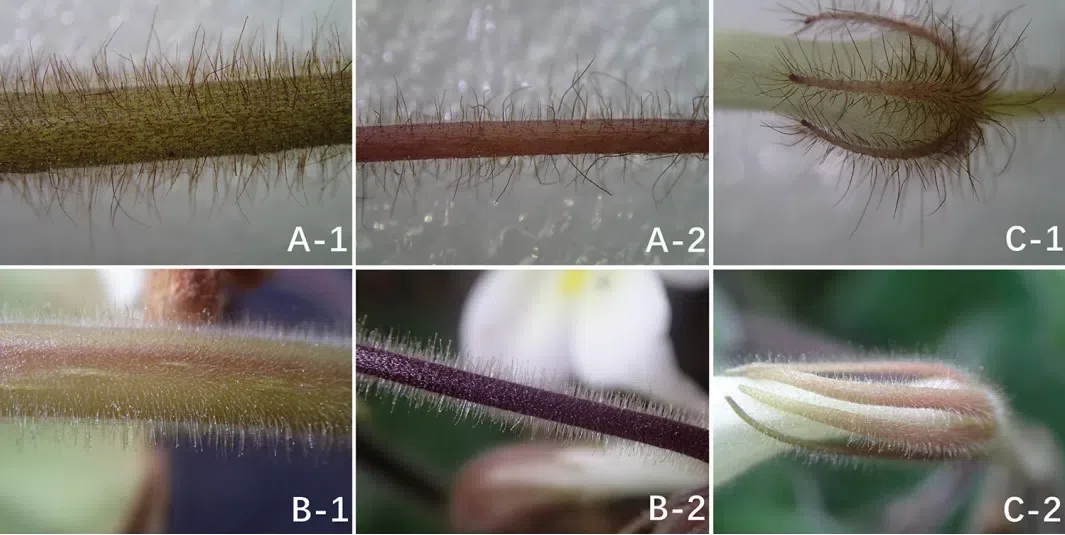

Figure 3. The difference of indumentum between PetrocodonrubiginosusY.G.Wei&R.L.Zhang, sp. nov. (A) and Pet. hechiensis (Y.G.Wei, Yan Liu &F.Wen) Y.G.Wei&Mich.Möller (B): densely curly rubiginous to ferruginous villous on surface of petiole (A–1), pedicel (A–2) and calyx lobes (C–1) and densely short glandular-pubescent and pubescent on surface of petiole (B–1), pedicel (B–2) and calyx lobes (C–2).